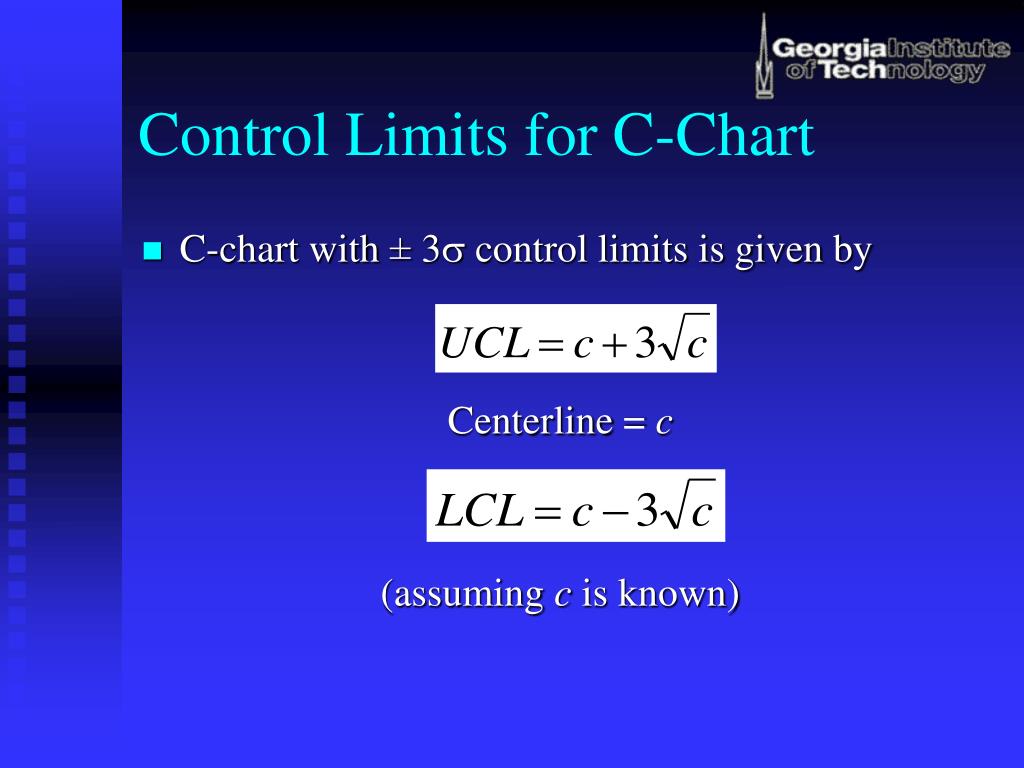
C Chart Control Limits . the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n The sample averages and the. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. control charts for discrete data. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. control charts generally have three parts:
from www.slideserve.com
control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n The sample averages and the. control charts generally have three parts: the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. control charts for discrete data. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small.
PPT IC Manufacturing and Yield PowerPoint Presentation, free download
C Chart Control Limits the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: control charts for discrete data. the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. The sample averages and the. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. control charts generally have three parts:
From www.youtube.com
SPC 4 c chart (Control Chart for number defective) YouTube C Chart Control Limits to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. control charts generally have three parts: Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c). C Chart Control Limits.
From classlibraryfruehauf.z19.web.core.windows.net
Range Charts Are Used Mainly With Attribute Data C Chart Control Limits Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n control charts generally have three parts: Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. The sample averages and the. control charts for discrete data. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. Web. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.youtube.com
Calculating Control Limits for a c chart by hand YouTube C Chart Control Limits control charts for discrete data. the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. control limits are the horizontal lines. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT IC Manufacturing and Yield PowerPoint Presentation, free download C Chart Control Limits The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. The sample averages and the. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. control charts generally have three parts: Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Control Chart Selection PowerPoint Presentation, free download C Chart Control Limits the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n control charts for discrete data. The sample averages and the.. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Ch 10_Quality Control_C Chart Control Limits C Chart Control Limits The sample averages and the. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. control charts for discrete data. Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n the upper control limit (ucl). C Chart Control Limits.
From www.bartleby.com
Control Limits bartleby C Chart Control Limits control charts for discrete data. Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. Web. C Chart Control Limits.
From robertmatthews.z19.web.core.windows.net
Control Chart X Bar C Chart Control Limits the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: The sample averages and the. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 17 Statistical Quality Control PowerPoint Presentation C Chart Control Limits The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. control charts for discrete data. Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. The sample averages and the. the upper control limit (ucl) and. C Chart Control Limits.
From slidetodoc.com
Chapter 6 Part 2 SPC Attribute Control Charts C Chart Control Limits Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. to use a c control chart, the opportunity. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT MIM 558 Comparative Operations Management PowerPoint Presentation C Chart Control Limits The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. The sample averages and the. control charts generally have three parts: control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. Sample averages, a centerline,. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Control Charts PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID996623 C Chart Control Limits control charts generally have three parts: Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. Cl = σ(count of defects per sample) / n The sample averages and the. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. control charts for discrete data. Web. C Chart Control Limits.
From datascienceplus.com
Implementation and Interpretation of Control Charts in R DataScience+ C Chart Control Limits control limits are the horizontal lines that are above and below the center line. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be large, but the actual number that occur must be small. the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Control Chart Selection PowerPoint Presentation, free download C Chart Control Limits the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: The sample averages and the. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. to use a c control chart, the opportunity for defects to occur must be. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.sixsigmadaily.com
Control Chart Construction Formulas for Control Limits C Chart Control Limits The sample averages and the. Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Operations Management Statistical Process Control Supplement 6 C Chart Control Limits control charts generally have three parts: Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. The sample averages and the. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. control charts for discrete data. Cl = σ(count of defects per. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT IC Manufacturing and Yield PowerPoint Presentation, free download C Chart Control Limits Sample averages, a centerline, and control limits. The control limits indicate whether a process is out of. The sample averages and the. the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the following formulas: to use a c control chart, the. C Chart Control Limits.
From www.statisticshowto.com
C Chart Definition, Formulas Statistics How To C Chart Control Limits control charts for discrete data. control charts generally have three parts: Used when identifying the total count of defects per unit (c) that occurred during the sampling period, the c. the upper control limit (ucl) and lower control limit (lcl) are calculated based on the average count of defects and the number of samples (n) using the. C Chart Control Limits.